Applied Energy Volume 306, Part B, 15 January 2022, 118072
Angelo Maiorino, Manuel Gesù Del Duca, Ciro Aprea
Department of Industrial Engineering, Universit`a di Salerno, Via Giovanni Paolo II, 132, 84084 Fisciano, Salerno, Italy
Advanced control methods proved they effectiveness in reducing energy consumption of refrigeration systems equipped with a variable-speed compressor, but they could not be suitable for fixed-speed compressors, which are usually controlled by a simple ON/OFF logic with a mechanical thermostat, which does not allow to optimize the performance of such devices.
Hence, a novel control method based on the use of Artificial Neural Networks to optimize the operations of refrigeration systems equipped with a fixed-speed compressor is proposed.
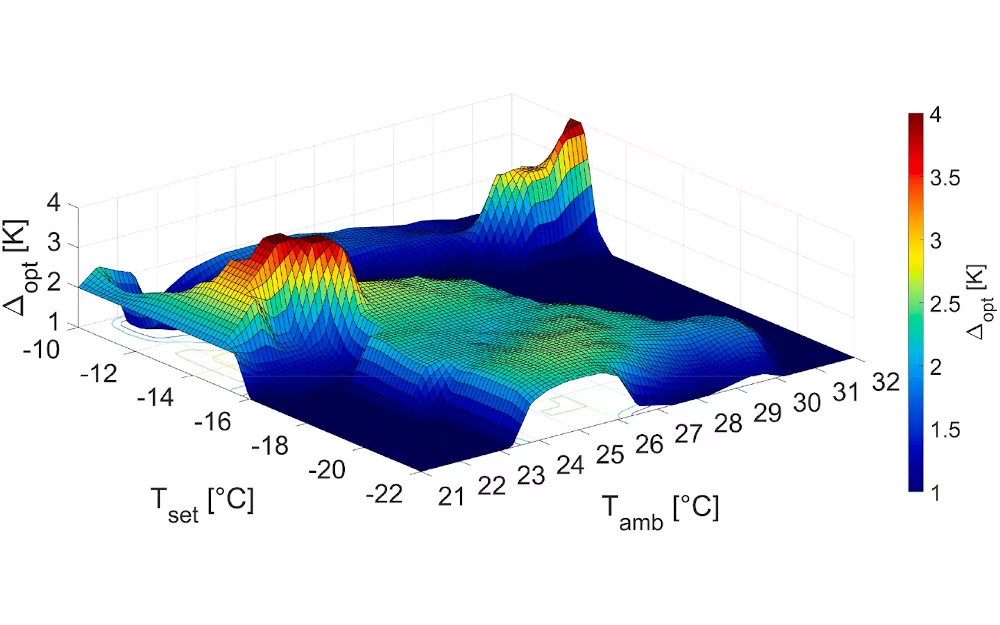
This technique uses an Artificial Neural Network, which stem from a three-step process, able to provide the ON/OFF control loop with the optimal hysteresis value accordingly to the requirement of the user, in terms of set-point temperature and optimization priority, and the ambient temperature.
The proposed control method was encoded in a microcontroller to test its effectiveness with a refrigeration system.
The results of the experimental tests demonstrated the great potential of this approach showing a reduction of energy consumption of 6.8% and 2.2% with no stored material and ambient temperatures of 25 ◦C and 32 ◦C, respectively.
Then, the introduction of 45 kg of stored material led to energy savings up to 13.4% and 6.6% with ambient temperatures of 25 ◦C and 32 ◦C, respectively.
Furthermore, it was evidenced that door openings and pick-and-place operations can reduce the positive effect of this approach, reducing the energy saving to 3.7%.
The results show that Artificial Neural Networks can be successfully applied to optimize the ON/OFF control loop of refrigeration systems, considering both plug-in and built-in solutions.
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect